On our main platform for VPS services, VirtFusion, the port ranges are fixed and pre-calculated for you on the outbound ports - but you can do any internal NAT IPv4 ports, as long as they're above port number 1024 (e.g. port 3490, port 6530, port 10600). With the exception of port 22 for SSH (on Linux OS templates) and 3389 for RDP (on Windows OS templates), we cannot guarantee ports below 1024 on a private IPv4 are operational or working - use them at your own risk.
IPv6 does not have this restriction and is always available, on all ports, usually except port 25 on some servers. You can reach out to our support if you'd like to unlock this port on IPv6.
How to Open Ports on the new VirtFusion NAT System
1. Login to the VirtPortal. The VirtPortal is available at virtportal.cfld.uk, where you shall insert your user and password.
If you don't have yet a password, or forgotten your VirtPortal password, you have two options: either access the WebStore Client Area and click on "Manage" and then, on the new screen, "Reset Panel Password", where you'll need to take notes on your password shown on-screen, and then reattempt the access to the VirtPortal; or outright require a new panel password on the VirtPortal itself on the login screen, using the "Forgot Password" option.
2. Access your VPS Area.
If it is already available and you've already installed your VPS operating system, it will look like this:
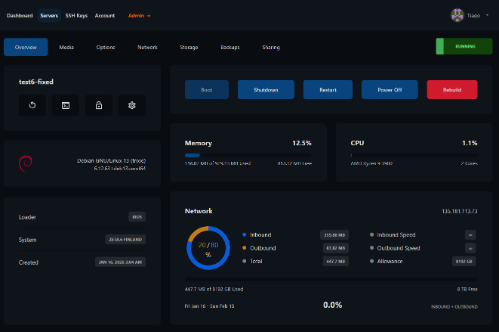
This is the standard dashboard for the VirtPortal. If you're not seeing this screen, you need to provide a name to your VPS and install an OS; if you wish to provide an ISO and install from an ISO, this will be available after the first install, on the "Media" menu, next to "Overview", on this screen.
3. Access your NAT Port Section
The following screen does not appear for full IPv4 VPS services.
In the "Network" menu seen above, and by scrolling the page, you'll see the following two sections: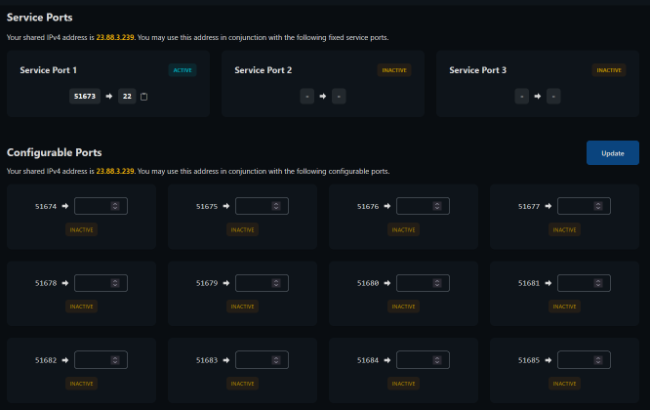
The Service Ports are the "+3" ports mentioned on your VPS product description. They're always provided upon purchase, cannot be changed, do depend on the chosen Operating System, and users will see the format as "xxxxx > xx", meaning that an outbound port number maps to another internal port number. On this image's example, port 51673 maps to the internal port 22, allowing you direct SSH access under Linux. But you may be seeing any other number prior to the ">" sign, and that is what you must follow. Your VirtFusion deployment e-mail will also have the exact port information, at any time.
Windows users will see something in the format of "51673 > 3389" - this belongs to the RDP service, the protocol for Microsoft Windows.
The Configurable Ports are the "20" ports mentioned on your VPS produt description. Those are entirely configurable and changeable to your liking, and the same rule applies: the format is still "xxxxx >", only with the difference that you can input any other number above 1024 on this field. Any changes done on NAT may take up to 15 minutes to be assumed- or, in special circumstances, even higher than that. The linked article on the underlining/bold mentions our NAT policies, at present.
Any services not prohibited by the Fair Usage Policy, the Terms & Conditions, or any other upstream policies or product-specific restrictions, can be run on these NAT ports. Be sensible on the services you're running on NAT IPv4 - there's always a shared IP, and as with everything shared and unless stated otherwise on the product description, any illegal/non-regular activity may render service suspension or termination, per our FUP/T&Cs, not to mention the issues you may be causing to other customers by your own activity, whichever it is. Responsibility on NAT IPv4 utilization is essential for everyone.
Are VirtFusion opened ports TCP or UDP?
The available port range can be used for TCP or UDP at will, and the 20 ports can be used for any protocols.
Last Update: 02-02-2026